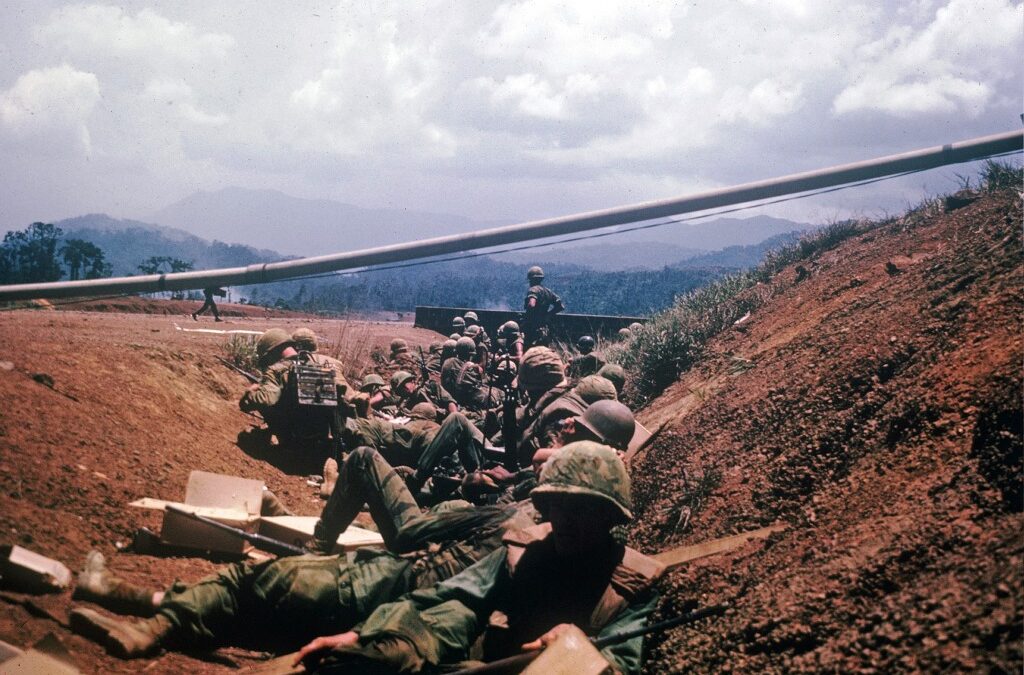
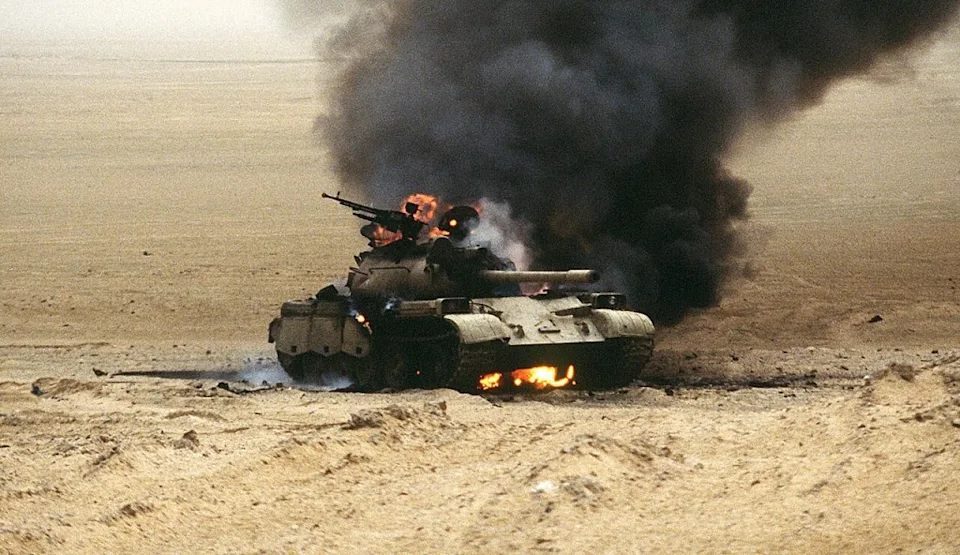
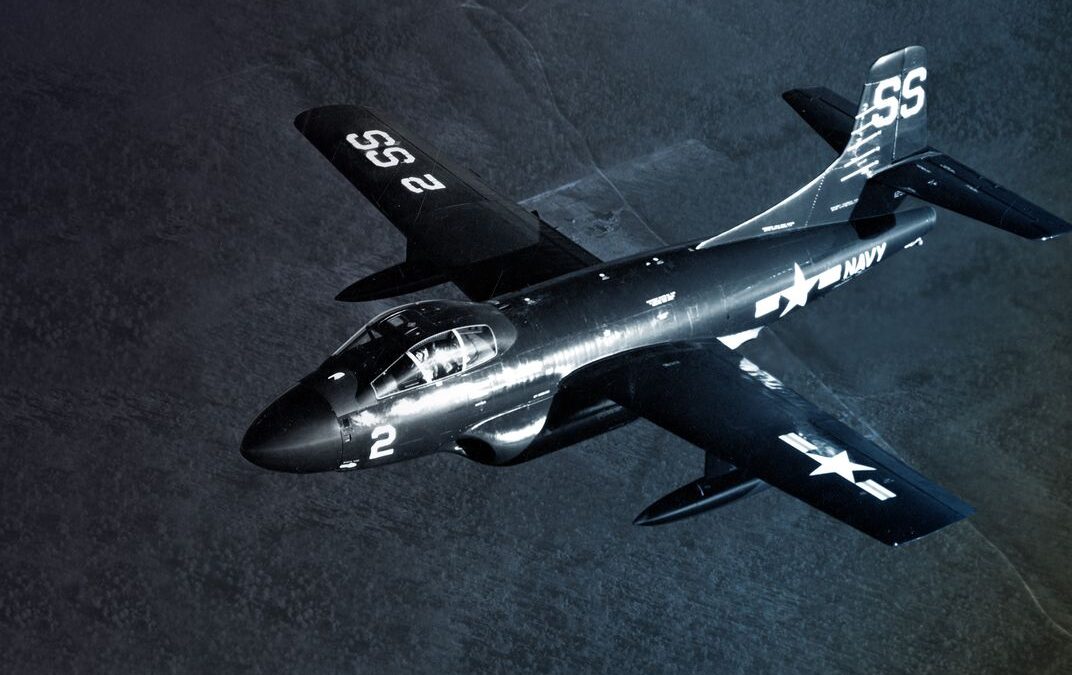
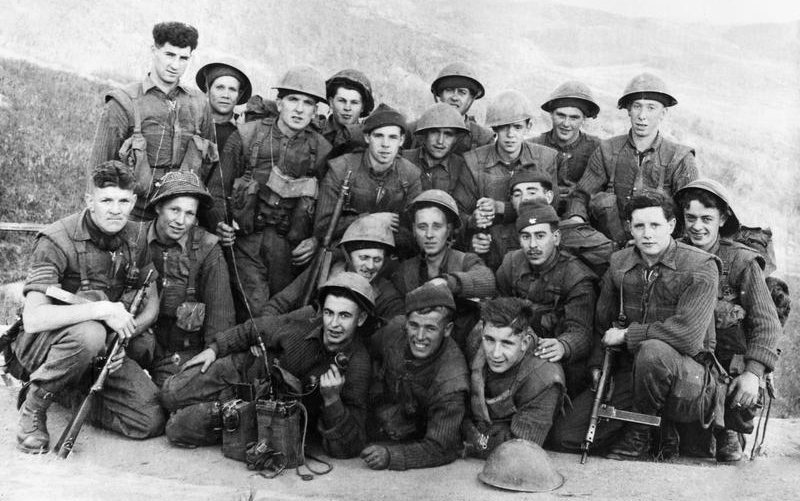
Kham Duc Special Forces Camp (A-105), was located on the western fringes of Quang Tin Province, South Vietnam. In the spring of 1968, it was the only remaining border camp in Military Region I. Backup responsibility for the camp fell on the 23rd Infantry Division (Americal), based at Chu Lai on the far side of the province. Battle Of Ngok Begins As Kham Duc Becomes Outpost The camp had originally been built for President Diem, who enjoyed hunting in the area. The 1st Special Forces Detachment (A-727B) arrived in September 1963 and found the outpost to be an ideal border surveillance site with an existing airfield. The camp was located on a narrow grassy plain surrounded by rugged, virtually uninhabited jungle. The only village in the area, located across the airstrip, was occupied by post dependents, camp followers, and merchants. The camp and airstrip were bordered by the Ngok Peng Bum ridge to the west and Ngok Pe Xar mountain, looming over Kham Duc to the east. Steeply banked...