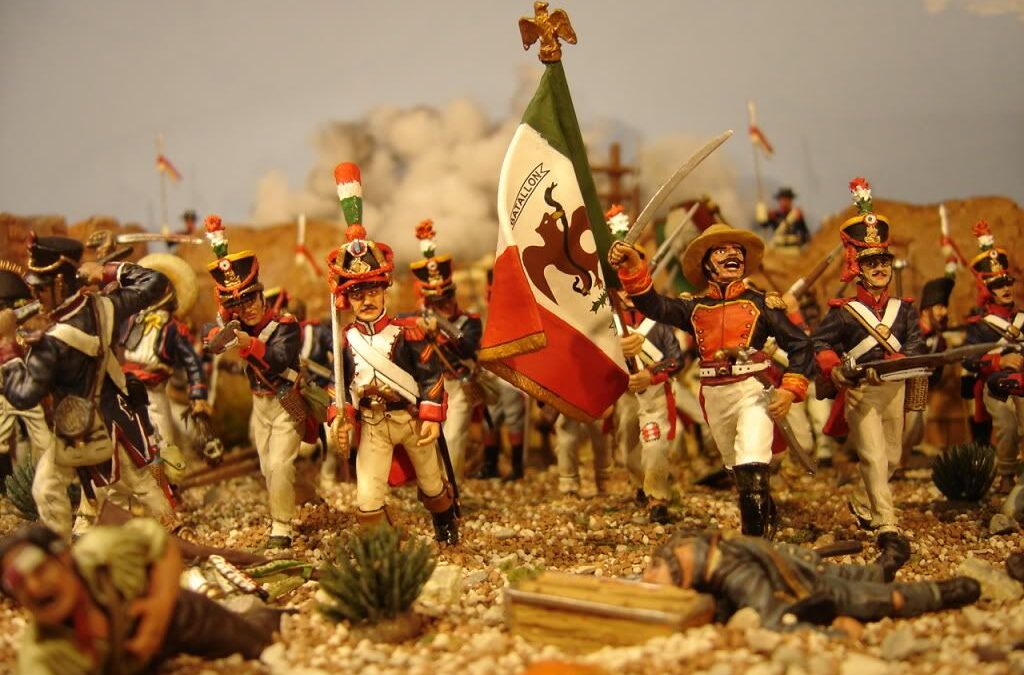
Few battles in American history resound so powerfully in our collective memory as that of the Alamo. The Battle of the Alamo had everything we could ever want in an epic story. It featured a handful of defenders fighting for freedom, facing down an overwhelming but cruel enemy, and among those defenders were some of America's most legendary names. When the defenders of the Alamo were killed to the last man, it inspired a country to take up arms and win their freedom, lest they all meet the same fate. The Texians who fought at the Alamo may not have won the battle, but their sacrifice helped win the war and freedom for their country. Background of the Battle of the Alamo For years before the battle, Texas enjoyed a swell of population and the autonomy to grow far from the heavy hand of government from Mexico City. When General Antonio Lopez de Santa Anna came to power in 1832 and changed all that. By 1835, he consolidated power and tried to rule through a more centralized...