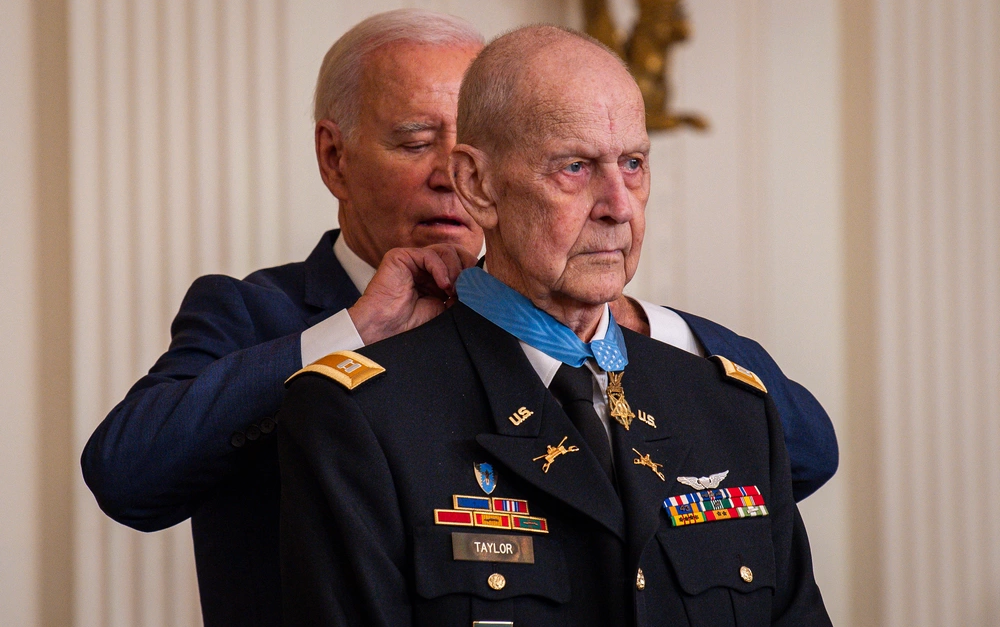
Larry Taylor's family had a long history of military service. His great-great-grandfather fought in the Civil War, his great-uncle fought in World War I, and his father and uncles served during World War II. When Larry attended the University of Tennessee in Knoxville, he joined the school's Reserve Officers Training Corps (ROTC) and carried on his family's longstanding military tradition. Larry L. Taylor Begins His Journey in the Vietnam War When he began his studies in 1962, the United States had only a token involvement in the uncertain future of South Vietnam. By the time he graduated in 1966, the U.S. was fully committed, with more than 380,000 ground troops in the country. Initially, he was commissioned as an armor officer. Though he graduated from the Army's armor school, he knew he could do more flying helicopters. Because of his critical moment of self-reflection, he would lead a daring rescue under heavy fire, saving the lives of his fellow soldiers and performing an...