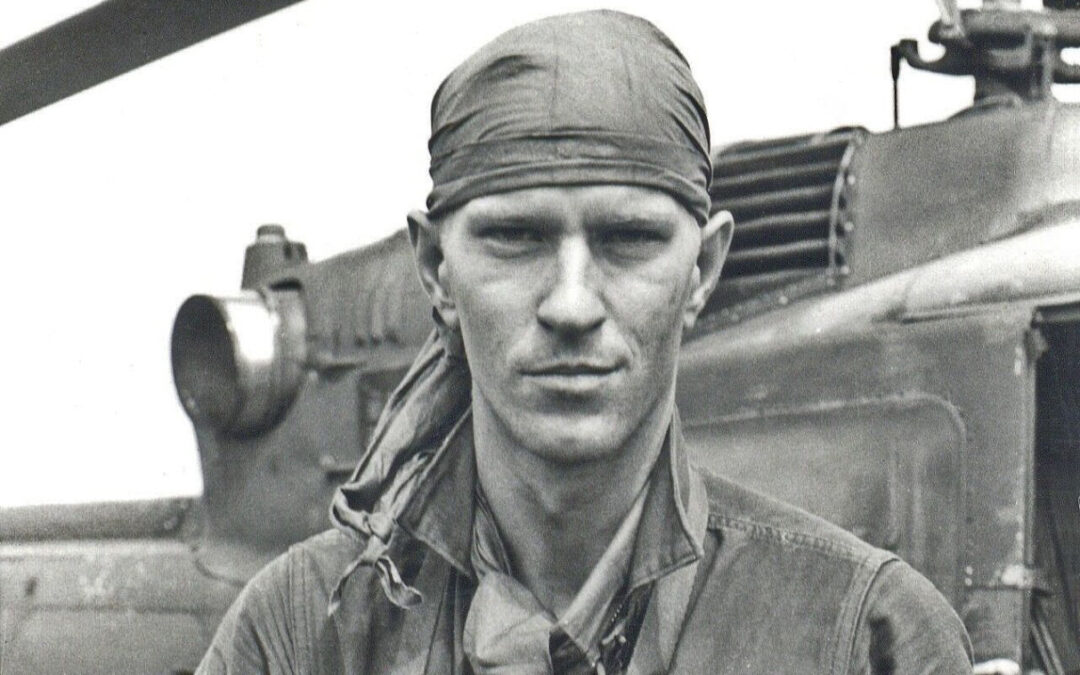
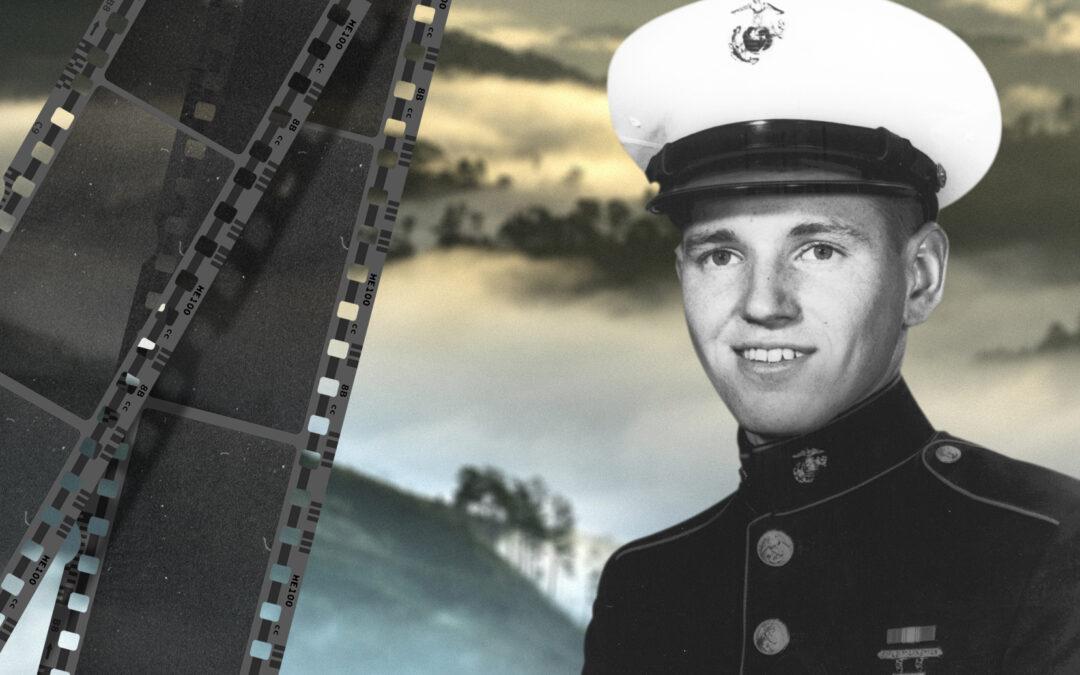
For 19-year-old Pat Finn, a Minnesota Marine with Item Co, 3rd Battalion, 5th Marines, the night seemed colder and darker than any of the others he'd experienced since landing in Korea. His Battalion had just arrived at a desolate, frozen lake he would remember for the rest of his life: the Chosin Reservoir. Chosin Reservoir Hit by a Devastating Surprise Attack As the sun went down on November 27, 1950, and temperatures sank to 20 degrees below zero, Marines at Yudam-ni, a small village on the west side of the Chosin Reservoir, hunkered down for what they hoped would be a quiet, uneventful night. "The war was all but over," Finn recalled in his diary written weeks later from a hospital bed in Japan. "You'll be home by Christmas," he'd been told. But his buddy, Eddie Reilly, wasn't buying it. In his usual pessimistic tone, he told Finn, "Pat, I don't like the look of all this, it sounds too good." For the next four hours, the two Marines scraped and dug into the frozen, rocky ground,...