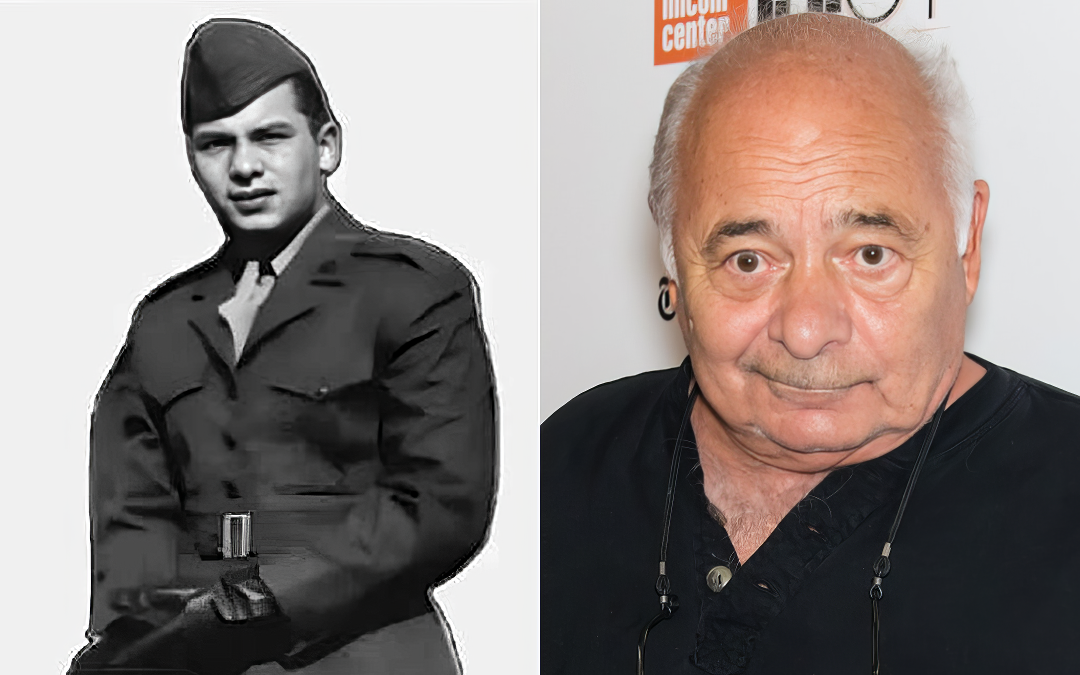
You may not recognize the name, but you'll recognize the face. Let's be honest: a Burt Young movie marathon is a day well spent. He appeared in more than 160 roles in 50 years in Hollywood, acting alongside the silver screen's most recognizable names: Jack Nicholson, Robert De Niro, and, of course, Sylvester Stallone. His credits include "Chinatown," "The Killer Elite" and "Once Upon a Time in America," along with his turn as Paulie in the 1976 film "Rocky." He continued in the role through all of the "Rocky" sequels, but it was his performance in the first film that earned him an Academy Award nomination for Best Supporting Actor. The Unlikely Journey from Queens Hoodlum to Hollywood Star Burt Young, born Gerald Tommaso DeLouise on April 30, 1940, in Queens, New York, USA, grew up in a family where his father wore many hats—a sheet metal worker, an iceman, and eventually a high school shop teacher and dean. He has Italian-American heritage, which added authenticity to...